Bile imbalance liver cancer is emerging as a critical area of research, highlighting the intricate link between bile acid metabolism and liver health. Recent studies have unveiled how disruptions in bile production and regulation can lead to severe liver conditions, notably hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the predominant form of liver cancer. Understanding the role of key molecular mechanisms, such as the FXR function and the YAP signaling pathway, is essential in uncovering potential therapeutic strategies. This research opens the door to innovative treatment interventions that could target the deleterious effects of bile acid imbalances. As we delve into the complexities of liver cancer, it becomes increasingly clear that maintaining proper bile acid levels is vital for preventing hepatic diseases and promoting overall liver health.
The relationship between disrupted bile acid homeostasis and liver malignancies is gaining significant attention, showing that an imbalance can precipitate severe hepatic disorders. In particular, conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) exemplify the consequences of disturbed bile production, where bile acids, crucial for digestion, take on a new and harmful role. Research focusing on important pathways like the FXR function and YAP signaling opens up promising avenues for understanding prevention and treatment options. As scientists investigate these connections, they aim to develop therapies that might restore bile balance and mitigate the risks associated with liver cancer. Ultimately, addressing bile acid metabolism could transform the landscape of liver disease management.
Understanding Bile Acid Metabolism
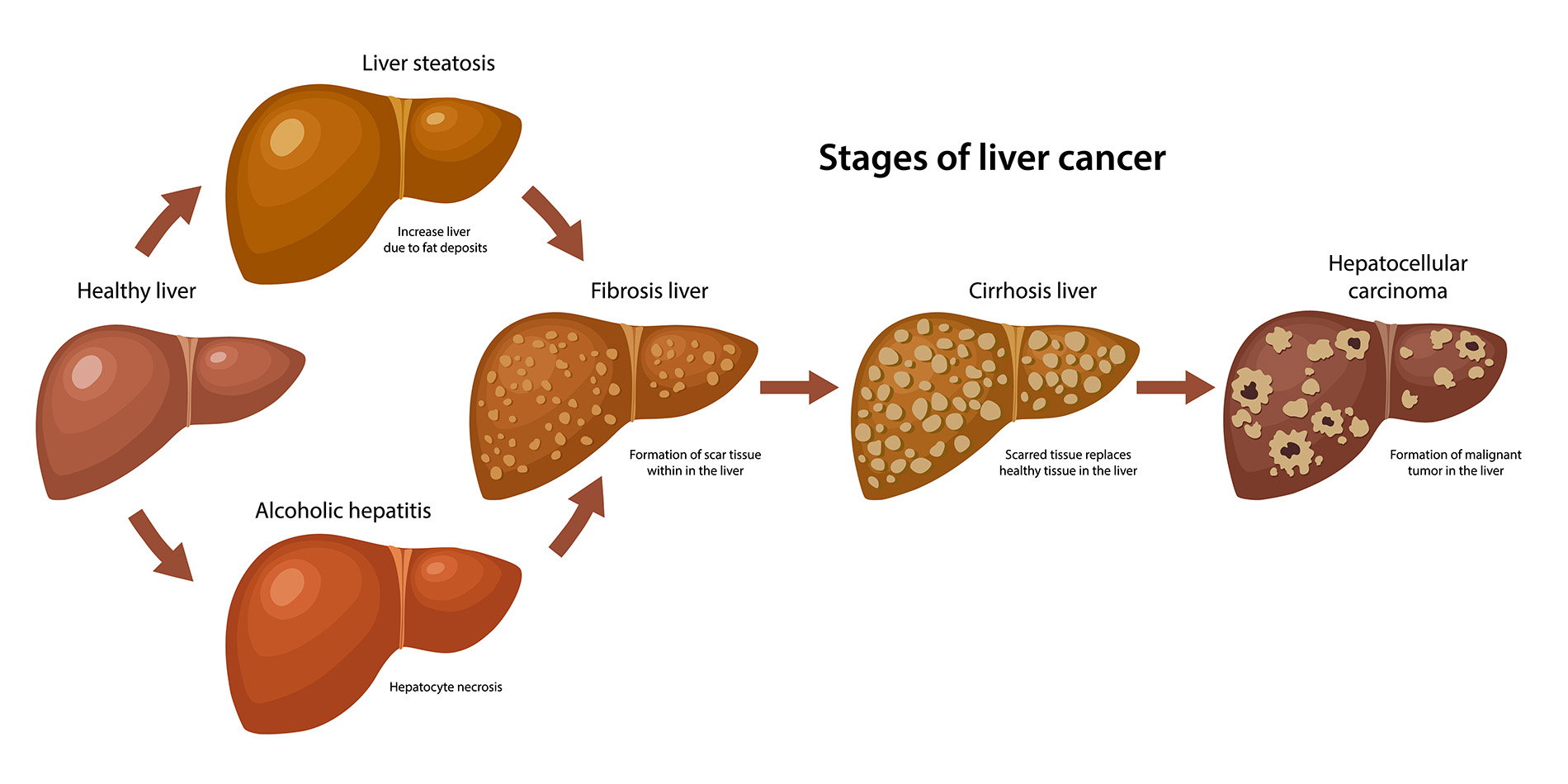
Bile acid metabolism is a crucial aspect of liver function and overall digestive health. Bile acids are synthesized in the liver from cholesterol and play a vital role in the emulsification of dietary fats, facilitating their absorption in the intestines. Disruptions in bile acid regulation can lead to severe consequences, including liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Maintaining the balance of bile acids is essential not only for proper digestion but also to mitigate potential toxicity in the liver.
Recent research has highlighted the hormone-like roles of bile acids, indicating their impact on metabolic processes beyond digestion. Abnormal bile acid levels can activate inflammatory pathways and contribute to fatty liver disease, a known precursor to HCC. Understanding how bile acid metabolism interacts with cellular signaling pathways, particularly the YAP signaling pathway, can elucidate the mechanisms behind liver cancer development and open new avenues for therapeutic interventions.
The Connection Between Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer
Recent findings emphasize the link between bile imbalance and the progression of liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). When bile acid levels become dysregulated, it can lead to liver damage, inflammation, and ultimately cancerous transformations. Researchers have identified that the YAP signaling pathway plays a significant role in this process by inhibiting a critical bile acid sensor known as FXR. This inhibition results in increased bile acid production, which accumulates in the liver and contributes to fibrosis and inflammation.
The study led by Yingzi Yang demonstrates that this pathway is not just a passive participant but actively influences bile acid metabolism and liver cancer progression. By reversing the repressive effects of YAP or enhancing FXR function, there are promising therapeutic implications for interrupting the cycle of bile acid imbalance that leads to liver cancer. These insights could pave the way for innovative treatments targeting bile acid homeostasis in cancer care.
Role of FXR in Bile Acid Regulation
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is a nuclear receptor that plays a crucial role in regulating bile acid synthesis and homeostasis within the liver. FXR activation helps to maintain the balance of bile acids by promoting their excretion and inhibiting their synthesis. This function is vital in preventing bile acid accumulation, which can lead to liver injury and conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent studies reveal that the FXR signaling pathway is tightly connected to other metabolic processes and signals within the liver, emphasizing its importance in liver health.
The disruption of FXR functions, particularly through the actions of YAP, underscores a critical mechanism by which bile acid metabolism can influence liver cancer development. Strategies that enhance FXR activity are being explored as potential therapeutic interventions. For instance, pharmacological agents that can activate FXR show promise in reducing bile acid toxicity and preventing liver fibrosis, potentially curbing the progression towards HCC.
YAP Signaling Pathway and Cancer Dynamics
The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway is integral to cellular growth and stability, and emerging evidence indicates its pivotal role in liver cancer dynamics. YAP is known for promoting tumorigenesis, yet its regulation of bile acid metabolism introduces a complex layer of interaction between metabolic dysregulation and cancer progression. By acting as a repressor of FXR, YAP inhibits normal bile acid signaling, leading to an excess of bile acids that contribute to liver inflammation and fibrosis, hallmarks of conditions that can culminate in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Understanding how YAP influences bile acid regulation opens new avenues for targeted therapies in liver cancer treatment. By modulating YAP’s activity or restoring FXR function, researchers hope to design interventions that can halt the progression of liver diseases associated with bile imbalance, such as HCC. Exploring this relationship further may provide actionable insights into therapeutic strategies that not only aim to combat cancer but also restore metabolic balance within the liver.
Potential Therapeutics for Liver Cancer Treatment
The findings from recent studies highlight several potential therapeutic avenues targeting the bile imbalance and related signaling pathways in liver cancer treatment. One promising approach involves enhancing the function of FXR, which may help to restore bile acid homeostasis and reduce liver inflammation and injury. Pharmacological agents that activate FXR can promote bile acid excretion, ultimately reducing the risk of fibrosis and cancer progression associated with excessive bile acid accumulation.
Additionally, inhibitors of YAP could serve as another import therapeutic strategy. By blocking YAP’s repressive influence on bile acid metabolism, it may be possible to establish a healthier balance of bile acids and inhibit the progression to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). These findings position FXR and YAP as critical targets in the future development of liver cancer therapies, highlighting the importance of understanding bile acid metabolism’s role in liver health.
Impact of Bile Acid Imbalance on Liver Inflammation
Bile acid imbalance has profound implications for liver inflammation, a key contributor to the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). When bile acids accumulate due to dysregulation of bile acid metabolism, they can cause direct toxicity to liver cells, triggering inflammatory responses. Chronic inflammation is known to promote cellular damage and transformations that give rise to liver cancer. Therefore, maintaining a balanced bile acid pool is crucial for preventing liver injury and associated inflammatory cascades.
Recent studies have shown that components of the YAP signaling pathway play significant roles in modulating liver inflammatory responses triggered by bile acid imbalance. By understanding how this signaling pathway interacts with bile acid levels, researchers can develop targeted strategies to mitigate liver inflammation and reduce the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma. Effective management of bile acid levels could be an essential part of treating liver inflammation and preventing cancer progression.
Cell Signaling Mechanisms in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Cell signaling mechanisms are foundational in understanding liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The interplay between various signaling pathways, such as the Hippo/YAP pathway, can greatly influence the fate of liver cells, including their growth, repair, and capacity to respond to injury. Disruption in these pathways can tip the balance towards malignancy, underlining the importance of precise regulation in maintaining liver health and preventing cancer.
Research has increasingly focused on how these signaling pathways integrate with bile acid metabolism, revealing critical insights into the molecular underpinnings of HCC. By identifying key players such as FXR and YAP, scientists can target these pathways for therapeutic interventions, aiming to restore normal signaling functions and inhibit tumor progression. This integration of cell signaling and metabolism research opens new opportunities for developing treatments that address both the metabolic aspects of liver health and cancer biology.
Forward-Looking Strategies to Combat Liver Cancer
As research advances, forward-looking strategies in combating liver cancer focus on an integrated approach that combines understanding of bile acid metabolism with cell signaling pathways. The interplay between bile imbalance, FXR function, and YAP signaling opens valuable pathways for intervention. By targeting these mechanisms, researchers aim to develop promising treatments that can effectively manage liver conditions and potentially reverse the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
New pharmacological solutions aimed at enhancing FXR activity or inhibiting YAP’s repressive effects are in development, showcasing an exciting frontier in liver cancer treatment. As scientists continue to unravel the complexities of bile acid metabolism, the potential for innovative therapeutic strategies that leverage these insights looks promising, paving the way for improved outcomes for patients suffering from liver cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does bile imbalance play in the development of liver cancer?
Bile imbalance is linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), as it disrupts bile acid metabolism. When bile acid levels become excessive due to factors such as YAP activation, it can lead to liver injury, inflammation, and ultimately promote tumor formation. Understanding this relationship is crucial for developing new treatment strategies.
How does FXR function relate to bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
FXR, or Farnesoid X receptor, is a nuclear receptor critical for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. Dysregulation of FXR function, often due to changes in the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway, inhibits its ability to regulate bile acids properly, leading to imbalance and increased risk of liver cancer, including HCC.
What is the connection between the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway and bile imbalance in liver cancer?
The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway is crucial in regulating cell growth and bile acid metabolism. YAP activation signifies a disruption in FXR function, leading to excessive bile acid production. This imbalance can contribute to liver cancer development by promoting inflammation and liver damage, highlighting a potential target for treatment.
Can enhancing FXR function help prevent liver cancer associated with bile imbalance?
Yes, enhancing FXR function can potentially prevent liver cancer by restoring bile acid homeostasis. Targeting the repressive activity of YAP or stimulating FXR offers a promising approach to mitigating liver damage and diminishing the progression of liver cancer linked to bile imbalance.
What experimental approaches are used to study the effects of bile imbalance on liver cancer?
Researchers employ molecular, cellular, genetic, and genomic approaches to investigate the effects of bile imbalance on liver cancer. These studies often focus on the interplay between YAP signaling and FXR function, aiming to understand their roles in bile acid metabolism and cancer progression.
Why is bile acid metabolism important in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
Bile acid metabolism is vital in HCC because imbalances in bile acids can lead to toxic accumulation in the liver, provoking inflammation and injury. Understanding these metabolic pathways allows researchers to identify potential therapeutic targets to prevent or treat liver cancer effectively.
What are potential treatment strategies targeting bile acid imbalance in liver cancer?
Potential treatment strategies include pharmacological agents that activate FXR, inhibit YAP’s repressive functions, or enhance bile acid export proteins. By addressing bile acid imbalance, these strategies could reduce liver damage and hinder the progression of liver cancer.
How can understanding bile acid metabolism influence future liver cancer therapies?
Understanding bile acid metabolism can greatly influence future liver cancer therapies by identifying specific molecular targets such as FXR and YAP. By manipulating these pathways, novel treatments may emerge that can effectively manage or even reverse liver damage and combat hepatocellular carcinoma.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | A critical imbalance in bile acids may lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The liver produces bile which helps digest fats. |
| Key Molecular Switch | The study identifies YAP as a key molecular switch that disrupts bile acid metabolism and promotes liver cancer. |
| Role of YAP | YAP inhibits FXR, a nuclear receptor essential for regulating bile acid homeostasis. |
| Treatment Implications | Potential treatments include enhancing FXR function and promoting bile acid excretion to prevent liver damage. |
| Research Methods | The Yang Laboratory uses molecular and genetic approaches to investigate cell signaling in liver health and disease. |
Summary
Bile imbalance liver cancer is a critical health concern, particularly linked to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent studies have identified a crucial molecular switch, YAP, that disrupts bile acid metabolism and contributes to liver cancer progression. Understanding this relationship between bile acids and liver cancer enhances the potential for targeted treatments, providing hope for better management of liver health.