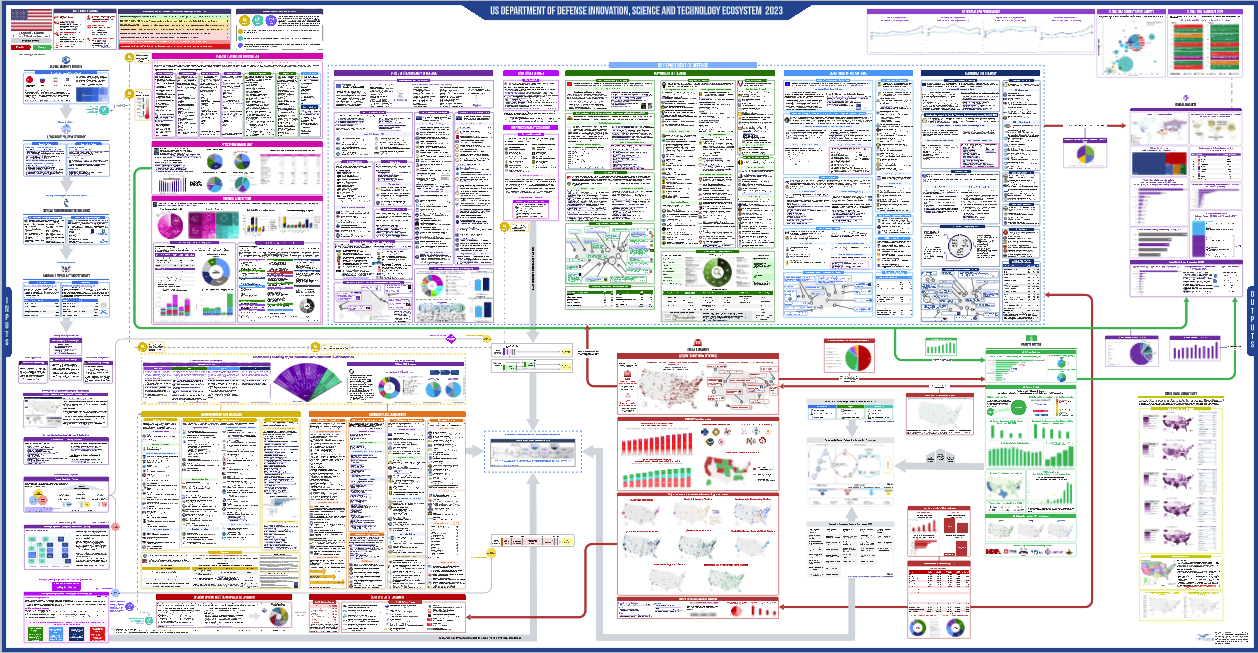
The U.S. innovation ecosystem stands as a beacon of creativity and progress, notably in the realm of biomedical research. This thriving landscape has its roots in the collaborative efforts of public-private partnerships, particularly during critical events like World War II, when federal funding fueled unprecedented technological advancements. The synergy between government initiatives and academic pursuits has cultivated a fertile ground for breakthroughs in health and medicine. As the nation confronts the current complexities surrounding funding allocations, the historical context of this symbiotic relationship highlights its significance in fostering innovations that have transformed lives. With a commitment to nurturing such collaborations, the U.S. innovation ecosystem continues to inspire and set standards for global practices in biomedicine and beyond.
The American landscape of technological and scientific advancement, often referred to as the innovation network, is characterized by its dynamic interplay of governmental, academic, and industrial entities. This framework not only drives efficiency and progress in medical discoveries but also catalyzes the evolution of public-private research alliances. The historical backdrop of U.S. biomedical breakthroughs reveals a profound legacy of cooperation, particularly rooted in war-driven innovations. As debates arise concerning federal contributions to research initiatives, it’s crucial to remember how these partnerships fundamentally shaped the healthcare sector over decades. The technological revolution spawned within this ecosystem continues to hold promise for future advancements in various fields.
The Roots of the U.S. Innovation Ecosystem
The U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly its biomedical research sector, is often regarded as a model globally, rooted in a historic collaboration between the government and academia. This partnership began during World War II, when the federal government recognized the urgency of mobilizing scientific resources to meet military needs. Scientists from universities and research institutions were enlisted to develop essential wartime technologies. This initiative laid the groundwork for extensive public-private partnerships that would dominate U.S. innovation for decades to come. From the creation of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) to pivotal breakthroughs like penicillin, the collaborative approach effectively transformed how scientific research was conducted in America.
The significance of this partnership transcended the war, as it initiated an era of unprecedented technological advancements and economic growth. Post-war, the collaboration among federal agencies, universities, and private industry led to the establishment of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which would become a cornerstone in biomedical research funding. Over the years, this unique ecosystem has evolved and adapted, fostering innovation not only in medicine but across multiple sectors. The success of World War II efforts laid a critical foundation for what is now one of the most advanced and productive innovation systems globally, positioning the U.S. as a leader in various scientific fields.
Public-Private Partnerships: A Key Driver
Public-private partnerships have been instrumental in the evolution of the U.S. biomedical research landscape. These collaborations leverage the strengths of academic institutions, federal funding, and private enterprises to accelerate innovation and drive meaningful advancements in public health. The symbiotic relationship has enabled universities to access vital resources and funding that would otherwise be unattainable. This has led to significant technological advancements in fields such as gene therapy, cancer treatment, and infectious disease control. As research initiatives receive federal backing, it results in an environment conducive to dynamic knowledge exchange between sectors, fostering creativity and cutting-edge solutions.
The effectiveness of these partnerships can be seen in the rapid response to health crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, where an unprecedented collaboration between the government and private firms led to the swift development of vaccines and treatments. These partnerships not only respond to immediate health needs but also contribute to the broader U.S. innovation ecosystem by sustaining continuous research and development. As the landscape of biomedical research evolves, maintaining this collaborative framework remains essential for nurturing the next generation of technological breakthroughs and ensuring that the U.S. remains at the forefront of global innovation.
Challenges to Federal Funding in Biomedical Sciences
Amid growing scrutiny of federal funding in the biomedical sector, significant concerns have emerged regarding potential cuts and their implications for innovation. Recent proposals to limit reimbursement for indirect research costs at prestigious institutions like the NIH could hinder the capacities of researchers and disrupt the longstanding collaborative frameworks established over the decades. Such changes may have a chilling effect on biomedical research, leading to reduced productivity in an ecosystem heavily reliant on federal funding for research grants that fuel innovation and discovery.
Additionally, the complexity of navigating federal funding policies often discourages academia from pursuing ambitious research projects, stifling the spirit of innovation. As highlighted in discussions with experts, sustaining robust federal support is critical not only for financing specific projects but also for establishing an environment where learning, experimentation, and technological advancements thrive. Without adequate federal investment in the biomedical research ecosystem, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries that can improve health outcomes and enhance economic growth may dwindle significantly.
The Historical Context of Biomedical Innovation
Understanding the history of biomedicine provides insights into how the U.S. innovation ecosystem has developed into a leader in technological advancements. The formal structure of government-supported research in the United States began taking shape during World War II as officials recognized the necessity of scientific breakthroughs for military effectiveness. The establishment of organizations like the OSRD enabled a systematic approach to mobilizing scientific resources to combat not just external threats but also infectious diseases that plagued the military. This history illustrates how urgent societal needs can catalyze the growth of research infrastructures, paving the way for future advancements.
Following the war, the momentum created by these initiatives continued to propel biomedical research forward, backed by ongoing federal funding and an integrated approach among universities, industry, and government agencies. Many of the breakthroughs arising from this period led to foundational changes in public health, including the establishment of regulatory bodies to ensure drug safety and efficacy. This evolving narrative of biomedical innovation underscores the importance of sustaining a dynamic interplay between federal funding and academic research while recognizing its historical inadequacies that necessitated a proactive response to public health challenges.
Technological Advancements in Biomedicine
The U.S. innovation ecosystem has witnessed an incredible trajectory of technological advancements in biomedicine, largely due to its sustained commitment to public-private partnerships. Innovations such as advanced imaging technologies, personalized medicine, and genome editing are testaments to a system that promotes extensive research collaboration. By harnessing the expertise of diverse stakeholders, the U.S. has managed to push the boundaries of what is achievable in healthcare, providing solutions that were unimaginable just a few decades ago. This ecosystem enables rapid translation of scientific discoveries from the laboratory to practical applications that directly impact patient care.
As biomedicine continues to evolve, new challenges arise that require innovative solutions. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in drug discovery processes is one example of how technological advancements are revolutionizing research practices. These tools not only streamline the discovery pipeline but also enhance the precision and efficiency of developing targeted therapies. Maintaining a robust framework of collaboration among various sectors will be essential for furthering these advancements, ensuring continued leadership in global biomedicine and addressing emerging health challenges, including pandemics and chronic diseases.
Training the Next Generation of Scientists
Efforts to sustain the U.S. innovation ecosystem also focus on training the next generation of scientists, which is vital for maintaining the momentum of biomedical research advancements. Universities play a crucial role in this process by nurturing young talent through graduate and postdoctoral programs that emphasize research and innovation. By involving students in public-private partnerships, these institutions equip them with the necessary skills and experiences applicable to real-world challenges. Engaging young scientists in significant projects fosters their development as future leaders in biomedicine and beyond.
Moreover, historical precedents suggest that the wartime mobilization of scientists led to a wealth of knowledge and expertise that has been beneficial long after the conflict ended. Today’s training programs can build on this legacy, emphasizing collaborative research experiences that reflect the realities of modern biomedical challenges. By prioritizing mentorship and integrating inter-disciplinary perspectives, educational institutions can cultivate a workforce equipped to drive future innovations, ensuring that the U.S. remains at the forefront of scientific discovery.
Impacts of Biomedical Research on Public Health
The reciprocal relationship between biomedical research and public health has never been more evident as research initiatives have led to substantial improvements in health outcomes. Breakthroughs in the understanding of diseases and the development of new treatment modalities have drastically reduced morbidity and mortality associated with various health conditions. The U.S. innovation ecosystem, supported by vigorous federal funding, has enabled researchers to pursue a wide array of health challenges, from chronic disease management to infectious disease prevention, significantly enhancing overall public health standards.
Historically, events such as the development of antibiotics during World War II exemplify how biomedical research can have immense societal benefits. The collaboration exhibited during this period directly resulted in tools that saved countless lives and reshaped public health infrastructure. As we continue to face new health threats, the continued investment in biomedical research will be imperative for sustaining the gains achieved over the last century and ensuring the health security of future generations. A robust innovation ecosystem will provide the necessary resources to tackle emerging public health crises head-on.
Future Directions for U.S. Biomedical Innovation
As we look toward the future, the U.S. innovation ecosystem must adapt to changing landscapes and emerging challenges in biomedical research. This can be achieved through a focus on interdisciplinary collaboration across fields such as biotechnology, informatics, and engineering, leveraging advanced technologies to enhance the pace of discovery. Continuous federal investment will also be crucial, particularly as public-private partnerships evolve to address contemporary health issues and diversify the portfolio of biomedical innovation. Incorporating diverse perspectives and expertise will be vital to overcoming barriers in research and developing holistic solutions.
Moreover, fostering international collaborations can unlock new opportunities for scientific exchange and enhance the U.S.’s standing as a leader in global health innovation. While the domestic focus remains paramount, engaging with global partners allows for the sharing of resources and lessons learned, resulting in advancements that can benefit all. By prioritizing strategic partnerships and investing in cutting-edge technologies, the future of biomedical innovation in the U.S. holds immense promise, continuing to build on a legacy of scientific excellence and improved health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of federal funding in the U.S. innovation ecosystem for biomedical research?
Federal funding plays a critical role in the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in biomedical research. It supports essential academic research, fosters technological advancements, and drives public-private partnerships. Over several decades, federal grants have provided significant financial resources that enable innovation in medicine and public health, contributing to groundbreaking discoveries and maintaining the U.S. as a leader in the global biomedicine field.
How did World War II influence the growth of the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
World War II was a pivotal moment for the U.S. innovation ecosystem, as it catalyzed collaboration between the federal government, universities, and private industry. The urgent need for technological advancements during the war led to the establishment of organizations like the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), which facilitated federal funding for research, resulting in major breakthroughs, including the mass production of penicillin. This model of public-private partnerships laid the groundwork for ongoing innovation in biomedicine.
What are some technological advancements driven by the U.S. innovation ecosystem in biomedicine?
The U.S. innovation ecosystem in biomedicine has driven numerous technological advancements, including the development of antibiotics, vaccines, and advanced medical devices. The collaboration between federal agencies, research institutions, and the pharmaceutical industry has resulted in revolutionary treatments for infectious diseases, cancer therapies, and improved surgical techniques, significantly enhancing public health outcomes and establishing the U.S. as a global leader in medical innovation.
Why are public-private partnerships significant to the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Public-private partnerships are essential to the U.S. innovation ecosystem because they leverage the strengths of both sectors to facilitate research and technological development. These collaborations enhance resource sharing, align academic research with industry needs, and promote innovation in biomedicine. Moreover, they provide a framework for sustained federal funding, which has been crucial for driving advancements and improving patient care while fostering economic growth in the process.
What historical changes have shaped the current U.S. innovation ecosystem in biomedicine?
The current U.S. innovation ecosystem in biomedicine has been shaped by significant historical changes, particularly the collaborative initiatives that began during World War II. The establishment of federal funding mechanisms and research partnerships allowed for the systemic development of biomedical research infrastructure. Over the decades, this evolved into a robust network that involves universities, industry players, and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), enabling a continuous flow of innovation and responsiveness to public health challenges.
What challenges does the U.S. innovation ecosystem face today regarding federal funding for biomedical research?
Today, the U.S. innovation ecosystem faces challenges concerning federal funding, particularly regarding proposed budget cuts and limitations on reimbursement for indirect research costs in biomedical sciences. These changes could hinder the ability of universities and research institutions to maintain and expand their projects, potentially stalling technological advancements and impacting the overall quality of research within the biomedicine sector.
How has the relationship between academia and federal funding evolved in the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
The relationship between academia and federal funding in the U.S. innovation ecosystem has evolved from a sporadic, limited interaction in the early 20th century to a deeply integrated partnership post-World War II. This transformation has allowed federal funding to support not only large-scale projects but also the training of new scientists, fostering innovation and encouraging universities to undertake ambitious research initiatives that contribute significantly to the field of biomedicine.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Origin of U.S. Innovation Ecosystem | The partnership between the federal government and academia began during World War II when scientists were mobilized to develop new technologies for the military. |
| Federal Role | The federal government has historically funded research that spurs private sector development, leading to breakthroughs in various fields. |
| Key Developments | Achievements during WWII, particularly in medicine (e.g., mass production of penicillin), laid the groundwork for future innovations. |
| Impact on Biomedicine | The existing U.S. innovation system in biomedicine involves collaboration among universities, the life sciences industry, and the NIH. |
| Current Challenges | Recent debates about federal funding and reimbursement for research costs may threaten the ongoing success of the ecosystem. |
| Importance of Training | World War II also contributed to the training of a new generation of scientists, fostering future leaders in research. |
Summary
The U.S. innovation ecosystem is a model admired globally, rooted in historical public-private partnerships that arose during World War II. This synergy not only catalyzed significant technological advancements, notably in biomedicine, but it also transformed how research and development are viewed as federally supported ventures. As current discussions on funding and policy reform unfold, preserving the effectiveness of this system is crucial to maintain U.S. leadership in innovation. The ongoing success and vitality of the U.S. innovation ecosystem are pivotal for continued national defense, economic growth, and global health advancements.